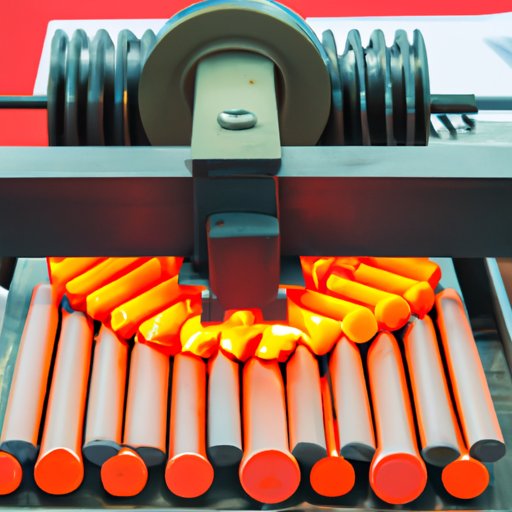
Exploring Induction Heating: What it is and How it Works
Induction heating is a process of heating a material through the application of an alternating magnetic field. In this process, an electrical current is passed through a coil that produces a magnetic field. The magnetic field then induces an electric current within the material being heated, which results in heat being generated. It is a fast and efficient way to heat materials with minimal risk of damage.
The process of induction heating is relatively straightforward. An alternating current is passed through a coil, generating a rapidly changing magnetic field. This magnetic field then induces an electric current within the material being heated. As the material heats up, the magnetic field collapses and the heat is released.
The benefits of using induction heating are numerous. It is fast and efficient, allowing for rapid heating of materials without the risk of damage. Additionally, induction heating can be used for a wide range of materials and applications, making it a versatile and cost-effective option for many industries.
An Introduction to Induction Heating Technology
Induction heating has been around since the late 19th century, when it was first developed by Nikola Tesla. Since then, advances in technology have made induction heating more efficient and cost-effective. Today, it is used in a variety of industrial applications, ranging from metal forging and heat treatments to joining metals and alloys.
There are several types of induction heaters available on the market today. These include high-frequency induction heaters, medium-frequency induction heaters, and low-frequency induction heaters. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, depending on the application and the material being heated.
An induction heating system typically consists of three main components: a power supply unit, a control system, and a heating coil. The power supply unit provides the necessary electricity to create the alternating magnetic field, while the control system regulates the power output and temperature. The heating coil is the core component of the system, as this is where the alternating magnetic field is created.
Benefits of Using Induction Heating in Industrial Applications
Induction heating offers several advantages over other traditional heating methods, making it an attractive option for many industrial applications. Here are some of the key benefits of using induction heating:
- Faster and More Efficient Heating: Induction heating is much faster than other traditional heating methods, such as convection or conduction. It requires less energy to heat materials, resulting in greater efficiency and lower costs.
- Reduced Risk of Damage to Parts: Because induction heating does not involve direct contact between the heating element and the material being heated, there is a reduced risk of thermal shock or other damage to the parts.
- Lower Energy Costs: Induction heating is more efficient than other traditional heating methods, resulting in lower energy costs.
Advantages of Induction Heating Over Other Heating Methods
Induction heating offers several advantages over other heating methods, making it an ideal choice for many industrial applications. Here are some of the key advantages of using induction heating:
- Higher Heating Rates: Induction heating is much faster than other traditional heating methods, making it an ideal choice for applications that require rapid heating of materials.
- Improved Safety: Because induction heating does not involve direct contact between the heating element and the material being heated, there is a reduced risk of thermal shock or other damage to personnel or equipment.
- Greater Flexibility: Induction heating can be used to heat a wide variety of materials, making it an ideal choice for many industrial applications.

A Guide to Choosing the Right Induction Heating System for Your Needs
Choosing the right induction heating system for your needs is essential to ensure optimal performance and safety. Here are some tips to help you select the best system for your application:
- Evaluating Your Requirements: Start by evaluating your requirements and determining the size, power rating, and type of induction heater that will best meet your needs.
- Determining the Power Rating: Consider the power rating of the induction heater, as this will determine how quickly and efficiently it can heat the materials.
- Understanding the Control System: Make sure the induction heater you choose has a reliable control system for regulating the power output and temperature.

Common Uses for Induction Heating in Manufacturing and Production
Induction heating can be used in a variety of manufacturing and production processes, including:
- Metal Forging and Bending: Induction heating is often used in metal forging and bending processes, as it allows for rapid heating of the metal without the risk of damage.
- Heat Treatments: Induction heating can be used to perform heat treatments on metals, such as hardening or tempering.
- Joining Metals and Alloys: Induction heating is often used to join metals and alloys, as it allows for rapid and efficient heating of the materials.
Conclusion
Induction heating is an efficient and cost-effective way to heat materials in industrial applications. It offers several advantages over other traditional heating methods, including faster heating rates, improved safety, and greater flexibility. If you’re looking for an efficient and reliable way to heat materials in your industry, induction heating is worth considering.